Oracle Automatic Storage Management and Cluster File System Archiving Scheme
The preferred configuration for Oracle RAC is to use Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) for a recovery area using a disk group for your recovery set that is different from the disk group used for your data files. When you use Oracle ASM, it uses an Oracle Managed Files naming format.
Alternatively, you can use a cluster file system archiving scheme. If you use a cluster file system, then each node writes to a single ___location on the cluster file system when archiving the redo log files. Each node can read the archived redo log files of the other nodes. For example, as shown in Figure 6-1, if Node 1 archives a redo log file to /arc_dest/log_1_100_23452345.arc on the cluster file system, then any other node in the cluster can also read this file.
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for more information about managing space in the recovery area and backing up archived redo logs with RMAN
Figure 6-1 Cluster File System Archiving Scheme
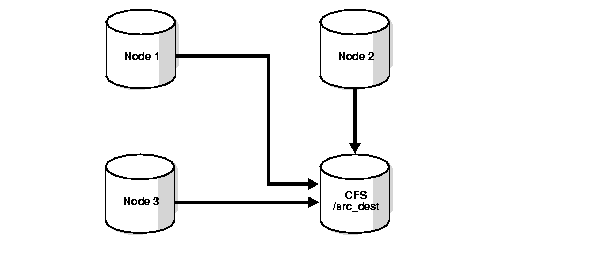
Description of "Figure 6-1 Cluster File System Archiving Scheme"
Note:
The archive log naming format in this example is only for a cluster file system example.
If you do not use a cluster file system, then the archived redo log files cannot be on raw devices. This is because raw devices do not enable sequential writing of consecutive archive log files.