在 LINQ to SQL 中,以开发人员编程语言表示的对象模型映射到关系数据库的数据模型。 然后,根据对象模型对数据进行操作。
在此方案中,不会向数据库发出数据库命令(例如 INSERT)。 而是更改值并在对象模型中执行方法。 如果要查询数据库或发送更改,LINQ to SQL 会将请求转换为正确的 SQL 命令,并将这些命令发送到数据库。
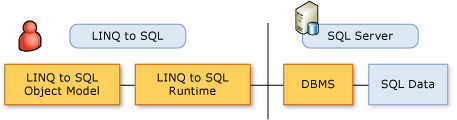
LINQ to SQL 对象模型中最基本的元素及其与关系数据模型中的元素的关系汇总在下表中:
| LINQ to SQL 对象模型 | 关系数据模型 |
|---|---|
| 实体类 | 表 |
| 类成员 | 列 |
| 关联 | 外键关系 |
| 方法 | 存储过程或函数 |
注释
以下说明假定你对关系数据模型和规则有基本的了解。
LINQ to SQL 实体类与数据库表
在 LINQ to SQL 中,数据库表由 实体类表示。 实体类就像你可能创建的任何其他类一样,只是通过使用将类与数据库表关联的特殊信息来批注该类。 通过向类声明添加自定义属性(TableAttribute)进行此批注,如以下示例所示:
示例:
[Table(Name = "Customers")]
public class Customerzz
{
public string CustomerID;
// ...
public string City;
}
<Table(Name:="Customers")> _
Public Class Customer
Public CustomerID As String
' ...
Public City As String
End Class
只能将声明为表(即实体类)的类实例保存到数据库。
有关详细信息,请参阅 Attribute-Based 映射的“表属性”部分。
LINQ to SQL 类成员与数据库列
除了将类与表关联之外,还可以指定字段或属性来表示数据库列。 为此,LINQ to SQL 定义 ColumnAttribute 属性,如以下示例所示:
示例:
[Table(Name = "Customers")]
public class Customer
{
[Column(IsPrimaryKey = true)]
public string CustomerID;
[Column]
public string City;
}
<Table(Name:="Customers")> _
Public Class Customer
<Column(IsPrimaryKey:=True)> _
Public CustomerID As String
<Column()> _
Public City As String
End Class
只有映射到列的字段和属性才会被保存到数据库中或从中检索。 那些未声明为列的列被视为应用程序逻辑的暂时部分。
该 ColumnAttribute 属性具有各种属性,可用于自定义表示列的这些成员(例如,将成员指定为表示主键列)。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Attribute-Based 映射的“列属性”部分。
LINQ to SQL 关联与数据库外键关系
在 LINQ to SQL 中,通过应用 AssociationAttribute 属性来表示数据库关联(如外键到主键关系)。 在以下代码段中, Order 类包含 Customer 具有 AssociationAttribute 属性的属性。 此属性及其特征为Order类和Customer类之间提供了关系。
下面的代码示例演示 Customer 类中的 Order 属性。
示例:
[Association(Name="FK_Orders_Customers", Storage="_Customer", ThisKey="CustomerID", IsForeignKey=true)]
public Customer Customer
{
get
{
return this._Customer.Entity;
}
set
{
Customer previousValue = this._Customer.Entity;
if (((previousValue != value)
|| (this._Customer.HasLoadedOrAssignedValue == false)))
{
this.SendPropertyChanging();
if ((previousValue != null))
{
this._Customer.Entity = null;
previousValue.Orders.Remove(this);
}
this._Customer.Entity = value;
if ((value != null))
{
value.Orders.Add(this);
this._CustomerID = value.CustomerID;
}
else
{
this._CustomerID = default(string);
}
this.SendPropertyChanged("Customer");
}
}
}
<Association(Name:="FK_Orders_Customers", Storage:="_Customer", ThisKey:="CustomerID", IsForeignKey:=true)> _
Public Property Customer() As Customer
Get
Return Me._Customer.Entity
End Get
Set
Dim previousValue As Customer = Me._Customer.Entity
If (((previousValue Is value) _
= false) _
OrElse (Me._Customer.HasLoadedOrAssignedValue = false)) Then
Me.SendPropertyChanging
If ((previousValue Is Nothing) _
= false) Then
Me._Customer.Entity = Nothing
previousValue.Orders.Remove(Me)
End If
Me._Customer.Entity = value
If ((value Is Nothing) _
= false) Then
value.Orders.Add(Me)
Me._CustomerID = value.CustomerID
Else
Me._CustomerID = CType(Nothing, String)
End If
Me.SendPropertyChanged("Customer")
End If
End Set
End Property
有关详细信息,请参阅 Attribute-Based 映射的“关联属性”部分。
LINQ to SQL 方法与数据库存储过程
LINQ to SQL 支持存储过程和用户定义的函数。 在 LINQ to SQL 中,将这些数据库定义的抽象映射到客户端对象,以便你可以以强类型的方式从客户端代码访问它们。 方法签名与数据库中定义的过程和函数的签名非常相似。 可以使用 IntelliSense 来发现这些方法。
调用映射过程返回的结果集是具有严格类型定义的集合。
LINQ to SQL 使用FunctionAttribute和ParameterAttribute属性将存储过程和函数映射到方法。 通过 IsComposable 属性可以区分表示存储过程的方法和表示用户定义函数的方法。 如果此属性设置为 false (默认值),则该方法表示存储过程。 如果设置为 true,则该方法表示数据库函数。
注释
如果使用 Visual Studio,可以使用对象关系设计器创建映射到存储过程和用户定义的函数的方法。
示例:
// This is an example of a stored procedure in the Northwind
// sample database. The IsComposable property defaults to false.
[Function(Name="dbo.CustOrderHist")]
public ISingleResult<CustOrderHistResult> CustOrderHist([Parameter(Name="CustomerID", DbType="NChar(5)")] string customerID)
{
IExecuteResult result = this.ExecuteMethodCall(this, ((MethodInfo)(MethodInfo.GetCurrentMethod())), customerID);
return ((ISingleResult<CustOrderHistResult>)(result.ReturnValue));
}
' This is an example of a stored procedure in the Northwind
' sample database. The IsComposable property defaults to false.
<FunctionAttribute(Name:="dbo.CustOrderHist")> _
Public Function CustOrderHist(<Parameter(Name:="CustomerID", DbType:="NChar(5)")> ByVal customerID As String) As ISingleResult(Of CustOrderHistResult)
Dim result As IExecuteResult = Me.ExecuteMethodCall(Me, CType(MethodInfo.GetCurrentMethod, MethodInfo), customerID)
Return CType(result.ReturnValue, ISingleResult(Of CustOrderHistResult))
End Function
有关详细信息,请参阅 Attribute-Based 映射 和 存储过程的函数属性、存储过程属性和参数属性部分。